- Home
- Free Samples
- Auditing
- HI6026 Audit, Assurance And Complianc...
HI6026 Audit, Assurance and Compliance Assessment Answer

HI6026
Weighting: 25% Total Assignment Marks: 50 marks
Purpose: This assignment is designed to assess your level of knowledge of the key topics covered in this unit
Description: Each week students were provided with three tutorial questions of varying degrees of difficulty. These tutorial questions are available in the Tutorial Folder for each week on Blackboard. The Interactive Tutorials are designed to assist students with the process, skills and knowledge to answer the provided tutorial questions.
Week 1
You are the audit manager of Overseas Explorer Ltd (OEL), which acquired the small proprietary company Local Pty Ltd (Local) on 30 June 2018. The price of the acquisition was agreed at $5 million, on the condition that OEL is satisfied with the financial records of Local. As Local is a small proprietary company, it has not prepared statutory financial reports or undergone an audit since its incorporation in 2016. However, Local has agreed to allow your firm, which is the auditor of OEL, to access its books and records. The CEO of OEL, Wendy Champion, has requested that your firm provide assurance on the following three items:
• The management accounts for the year ended 30 June 2017
• All transactions occurring from the date negotiations commenced until the settlement date, to ensure that all transactions were within the normal course of operations
• The financial report prepared at the acquisition date of 30 June 2018
In order to clarify your responsibilities, you requested that OEL indicate the level of assurance that they require for each item. Wendy replied that the financial report as at acquisition date is very important, as are the transactions since negotiations commenced, but that she is willing to have less work done on the previous year's management accounts.
Required: Indicate the type of engagement that will most likely be undertaken for each of the three tasks and the level of assurance to be provided. Explain your selections. (10 marks)
Week 2
You have been the auditor of Data Ltd for two years. Your auditor's report for Data for the year ended 30 June 2018 was unmodified, indicating that in your opinion the financial report gave a true and fair view. In August 2018, Data obtained a large loan from Better Bank Ltd, to provide additional working capital. Subsequently Data suffered severe trading difficulties and was placed into liquidation in late December 2018, with insufficient funds to repay the loan to Better Bank.
Required:
Outline a defense for your audit firm to any legal action taken by Better Bank to recover its loss. (10 marks)
Week 3
You are an audit manager at Hall & Associates, who have been approached to conduct the audit of Computer Games Ltd (CGL), a manufacturer of interactive computer games, for the year ended 30 June 2013.
Hall & Associates has not previously audited CGL's financial report, although it has undertaken other types of engagements for CGL. Last year CGL hired Hall & Associates to assist in the redesign of CGL's accounting software to ensure that internal controls over internet sales were adequate to ensure the confidentiality of customer data and accuracy of recording. The new software was implemented at the beginning of the current year and appears to be working satisfactorily. As part of this year's audit, you expect to review the internal controls at CGL, including the controls within the IT systems.
As part of CGL's financing arrangements with its bank, Easymoney Ltd, it has a loan covenant that stipulates that the quick asset ratio cannot be less than 1:1 or Easymoney Ltd has the right to withdraw all funding. The board has advised you that CGL's quick asset ratio is currently at 0.9:1 due to industrial action holding up the sale of goods imported from overseas. The board has asked you to ignore this temporary breach of the loan covenant, explaining that CGL is a stable and financially sound company, and that the ratio will return to a positive level on resolution of the industrial dispute. The board has indicated that unnecessarily disclosing this within the audit report would force it to reconsider its plans to use your audit firm for other engagements.
As a result of CGL's current cash flow difficulties, the board has requested that Hall & Associate's audit fee for 2013 be paid in CGL shares. The board has indicated that the market value of the shares will equate to the value of the audit fee charged by Hall & Associates.
The management of CGL is currently reviewing the structure of its audit committee to ensure that it complies with the requirements of the ASX Corporate Governance Principles and Recommendations. However, the board is confused by the reference in the ASX Corporate Governance Principles and Recommendations to both independent directors and non-executive directors, as they thought that they were the same thing. As a result, they have sought your advice concerning the structure of their audit committee.
Required:
- Identify and explain three separate key threats to Hall & Associates' independence that may arise under APES 110. (3 marks)
- For each independence threat identified in a) above, describe the course of action Hall & Associates needs to take to ensure compliance with APES 110. (7 marks)
Week 4
You are the audit senior responsible for the audit of Sampson Limited. You are currently planning the audit for the year ended 31 December 20X7. During your initial planning meeting held with the financial controller, he told you of the following changes in the company's operations.
- Due to the financial controller's workload, the company has employed a treasurer. The financial controller is excited about the appointment because in the two months that the treasurer has been with the company he has realised a small profit for the company through foreign-exchange transactions in yen.
- Sampson has planned to close an inefficient factory in country New South Wales before the end of 20X7. It is expected that the redeployment and disposal of the factory's assets will not be completed until the end of the following year. However, the financial controller is confident that he will be able to determine reasonably accurate closure provisions.
- To help achieve the budgeted sales for the year, Sampson is about to introduce bonuses for its sales staff. The bonuses will be an increasing percentage of the gross sales made, by each salesperson, above certain monthly targets.
- The company is using a new general ledger software package. The financial controller is impressed with the new system, because management accounts are easily produced and allow detailed comparisons with budgets and prior-period figures across product lines and geographical areas. The conversion to the new system occurred with a minimum of fuss. As it is a popular computer package, it required only minor modifications.
- As part of the conversion, the position of systems administrator was created. This position Is responsible for all systems maintenance, including data backups and modifications. These tasks were the responsibility of the accountant.
Required: For each of the scenarios above, explain how the components of audit risk (inherent, control or detection risk) are affected. (10 marks)
Week 5
Required: Provide four (4) possible explanations for the results for the various ratios for Solar Ltd and outline their implications for the audit. (10 marks)
Answer
Audit, Assurance and Compliance
Week 1
Assurance engagement
Assurance engagement refers to the practice of engagement exercised by practitioners to enable the company to understand and make opinions about the subject matter’s measurement. The opinions generated by the engagement practice induces the level of confidence in the user. There are two types of assurance that are provided by the professionals namely, limited assurance and responsible assurance. Responsible assurance takes the party into consideration who will provide all required information and data to the practitioners so that they can provide assurance to the user company. The information providing company is therefore, the responsible party (Knechel and Salterio, 2016). The objective behind exercising engagement assurance is to assure the users on the responsible party for the information and details which are presented to them.
Mainly three varied tasks are performed by the OEL’s audit manager. The financial analysis of the Local Pty Ltd will be undertaken to provide trustworthy assurance to the user company.
| Tasks | Types of level of assurance |
| The management accounts for the year ended 30 June 2017 | The CEO of the company OEL feels that the requirement to check the financial status of the company before 2016 is not required. However, she emphasizes on auditing the management accounts for the year ended 30 June, 2017. Therefore, auditors will be required to follow up the procedures that OEL agreed upon. |
| All transactions occurring from the date negotiations commenced until the settlement date | The OEL company’s CEO is not concerned about the transactions that happened before the negotiation date. However, the auditor requires the information of all the transactions happened to clarify from their responsibility. But the CEO only wants assurance to be provided of the transactions that occurred between the negotiation date to the final date of settlement. |
| Local’s financial report prepared at the acquisition date | To provide a high level of the confidence, the auditors are needed to perform an intense audit of the financial statements to reduce any chances of faults. The audit reports will assist the OEL company to make opinions regarding the value enhancement in the Local after its acquisition. |
Week 2
Liabilities and responsibilities of the Auditors
There are numerous responsibilities that an auditor has to provide to entrust the confidence of the users. The auditor has to derive reliable conclusions from the company’s financial reports. Along with the conclusions the auditor is also responsible for collecting reliable evidences to prove the drawn conclusions. However, even after such intensive research, the auditor is not expected to provide 100% assurance over the matter. Moreover, it is a risky way to depend completely on the predicted outcomes from the reports. Even though a 100% assurance cannot be provided, the auditors perform their function without any chance of faulting. This is because there are set standards of performing audits and the auditors has to follow them to avoid future complexities (Gimbar, Hansen and Ozlanski, 2016).
In the case of Data Ltd, the company was sanctioned a loan by Better Bank ltd on the basis of the data they received from the company. The company’s financial statements assured the bank that the loans will be repaid. But the Data Ltd came across difficulties in business therefore, now the company lack funds to pay back the loan. In this situation, the Data Ltd cannot hold the auditors accountable for this. The auditor only has access to the information that is made provided to him. He cannot provide audit statements beyond the provided data. Therefore, it is not the responsibility of the auditor to identify the faults and frauds of the company. He is only responsible for auditing the provided data. The Data Ltd company is therefore, solely responsible for their inability to payoff loans.
Week 3
Independence of auditor
The responsibility of the auditor is to perform auditing of the given reports by being independent of the unhealthy ways that can be used (Tepalagul and Lin, 2015). For example, biased towards the company. These factors should never be incorporated by the auditor while examining the reports and he should be aware of the limits of dependency and independency that the audit standards provide (Maroun, 2017). There are various threats to the independency that an auditor faces and some of them are explained below in the context of Hall & Associates:
- Self interest threat is defined by the APES 110 where, due to personal interest, the company may fall prey to the risks. The CGL company’s board has indicted to pay the fees of Hall & Associates in CGL shares. The auditing company therefore, may also receive some financial benefits due increase in the share values. The gain of financial interest is therefore, a self-generated threat by the company. however, there are ways in which the self interest threats can be safeguarded:
- Proper consultation and suggestions from professionals can protect the auditors from self interest threat.
- An effective action plan against the consequences of the threat can assist the auditors.
- If the problems do not solve, the auditor can also vacate his position.
- Intimidation threat is imposed by the CGL company on the auditing firm. This is identified because the company intimidates Hall & Associates to not disclose the asset ratio by saying that 0.9:1 is a temporary asset ratio and the company is financially sound. The company also indicated that it will rethink in engaging the auditors in other functions if they choose to disclose the actual asset ratio. The audit firms can use the following safeguards against the intimidation threat:
- Consultation and suggestions from experienced professionals.
- Audit team should include experienced members.
- If require, reorganize the engagement terms.
- Self-review threat is another threat that the auditing company faces. This is because, the Hall & Associates is engaged in providing the efficiency of the internal controls. It was involved in redesigning the software and now it is assigned to perform audit including the IT department of the company. in such cases the auditors can act bias towards their own work. Therefore, the threat of self-review can arise. The ways in which this threat can be avoided are:
- Involve independent auditors in the team who are not working in the same firm.
- Individual auditor should consider working properly and bias free as their responsibility.
- If problems persist, then auditor can vacate the position.
Week 4
Types of audit associated risks
There are three potential risks in audit functions. They can arise if the auditor is involved in providing irrelevant assurance to the company. The risks are (Abdullatif and Kawuq, 2015):
- Inherent risks: these risks are not under company’s control and material statements made in reports are the results of these risks.
- Control risks: these risks arise when internal control of the system is ineffective in detecting the errors in the statements.
- Detection risk: these risks are the result of ineffective functioning and performance of the auditor in identifying and correcting the misstatements in the reports.
In the current situation, the following risks of Sampson Limited are confirmed:
- The responsibility of handling the funds of the organization is fulfilled by the treasurer. The company’s financial controller is earning profits in the terms of foreign currency for the Sampson Limited. These foreign transactions are found to showcase inherent limitations (Samsonova and Humphrey, 2015). Therefore, the risk that exist in this case is inherent risk Control risk can also arise due to the factors like authorization towards funds.
- The financial controller of the company failed to provide appropriate provision because he could not determine the redeployment of the assets and this can give rise to inherent risk.
- A controlling system is required because the company has decided to provide bonus base on the sales of individual employee. If the controlling system face some technical issues then it might fail. Therefore, control risk is also displayed in this scenario.
- The probability of the controlling issues in the closing and opening balances can give rise to inherent risk. moreover, specialized trainings would be required for new software. This can result in control risks.
- Detection and control risk may rise because there is no provision for checking the functions of the controlling system. In such cases, the problems go unnoticed therefore, even auditors cannot detect the issues in the reports.
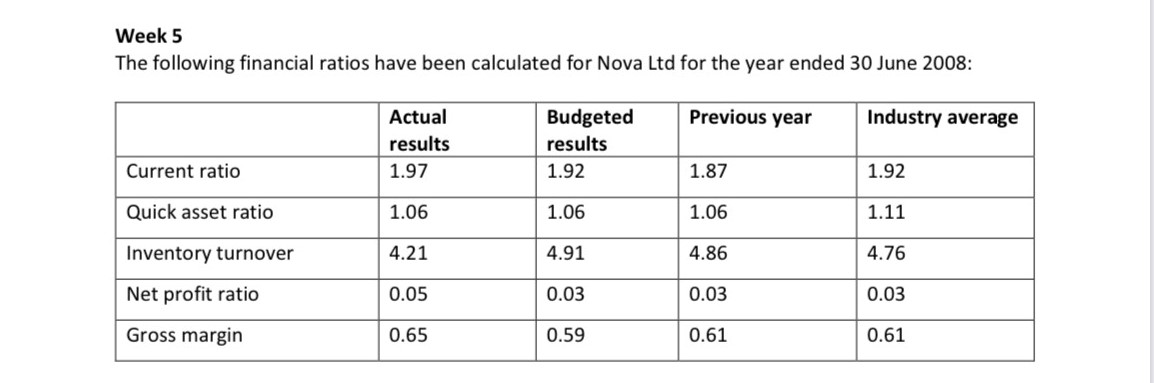
Week 5
Ratios
Ratios provide assistance in comprehending the firm’s financial results. The ratios also allows the firms to compare and analyze its performance (Arkan, 2016). The ratio analysis of the company Nova Limited are shown below in the table:
| Ratios | Description |
| Current | Nova Limited’s current ratio shows the ability of the company to payoff short-term loans and debts. |
| Inventory turnover | This ratio displays that in the present year, inventories are replaced 4.21 times by Nova Limited. This shows that the market has demand for company’s products. |
| Net profit | Income through different sources has allowed company to make profit 0.05 times. |
| Gross margin | The company was able to make profit 0.65 times from the currently operating functions. |
| Quick asset | the company can payoff short-term debts without needing prior realization of inventories. |










