- Home
- Free Samples
- Managerial Economics
- ECO600 Official Examination: Economic...
ECO600 Official Examination: Economics for Business and Finance Assessment Answer

| Subject Title | Economics for Business and Finance |
| Subject Code | ECO600 |
| Assessment Title | Official Examination |
Learning Outcomes | All of them |
| Assessment Type | Individual |
| Weighting | 40% |
| Word Count | Maximum 2,000 words |
| Submission Type | MS Word document |
| Final Examination Instructions | Instructions to Examination Candidates
|
Section 1: International trade and exchange rates (10 marks; length: 300-500 words)
The country you will focus on throughout this section is Indonesia.
Indonesia’s textile and leather footwear industry used to export a lot of shoes in the 1990s and 2000s. But it has faced tough competition from lower-cost producers in Vietnam and China. The government is considering protecting the industry from the full effects of free trade.
- Suppose this country has decided to protect the mentioned industry.
i) What trade protectionist policy (or policies) would you propose?
ii) Justify your action: discuss how it will benefit the industry or country
iii) What problems could arise from implementing it? How will you address the problems?
2. See Trading Economics. In the list, find the country’s name (the country in the case study above). Click on it. To view the trade balance for multiple years, set the chart’s duration to ‘25Y’ (25 years) or ‘Max’.
i) Comment on the country’s trade balance over the last several years— for example, is there a trend towards a surplus or deficit?
ii) Assume that this country reduces its official interest rates to lower levels than the USA does. All else remaining the same, will this country’s currency appreciate or depreciate versus the US dollar? Could it make this country’s exports more attractive or not?
3. See Harvard University’s Atlas of Economic Complexity.
- Enter the country name (the same country you examined above).
- Jump to the section on the page called ‘Economic Structure’. There click on and examine the country’s ‘Export basket’ (the products it exports).
- Then, click on and examine the country’s ‘Export complexity’ (how complex or high- value its export products are).
Develop a convincing new export plan.
i) Propose the export sectors or products whose complexity you feel could be improved. Argue why.
ii) How should those sectors or products be improved, in terms of complexity and value- added, so that they are globally competitive and can increase the country’s export earnings?
Section 2: Macroeconomic fundamentals and development economics (10 marks; length: no word limit— keep it brief)
The COVID-19 pandemic and lockdown has affected the Australian economy in many ways.
- Discuss how they might have affected each of the four components of Australia’s GDP (also known as aggregate demand, AD), other than government spending, G. (2 marks)
- Assess which of the three main types of unemployment might COVID-19 lockdowns be causing the most. Explain why. (2 marks)
- COVID-19 has affected both AD and aggregate supply (AS).
i)Draw a simple AS and AD diagram to show how they might have shifted. Draw in MS Word or draw on a piece paper, photograph, and paste the image in your answer document. (2 marks)
ii) Based on the diagram, comment on how GDP and the inflation rate would have changed. (2 marks)
4. For 2020, Australia’s inflation rate is expected to be 1.43%.
If a loaf of bread in the supermarket was A$4 at the start of 2020, what will its price be at the end of 2020?
Show your workings by typing it, or by writing it on a piece of paper, taking a photograph of it, and pasting it in your answer document. (2 marks)
Section 3: Development economics (10 marks; length: 300-500 words)
You are the newly elected prime minister of the Southeast Asian country Cambodia.
Cambodia is a Buddhist, low-middle-income country with a GDP of between US$20-30 billion. Its GDP growth was rapid: 8% each year of the last decade. Still, the GDP’s size is $5 billion smaller that Nepal’s and a tenth (1/10th) of neighbour Vietnam’s.
The same leader has been its prime minister for 35 years. Its population is 16 million. Of that, almost 5 million people are ‘near-poor’, meaning although above the poverty line, are vulnerable to becoming poor again if there are economic and other shocks (like COVID-19).
Though its capital city has shopping malls, nearly 80% of the population live in rural areas.
Only 57% of its population finish secondary education (high school); a quarter do not have good access to water; a third do not have access to good sanitation (toilet and sewage).
The economy was once almost entirely agricultural. Though less dependent on it, agriculture still makes up a quarter of its GDP. It mainly produces rice. Half the country is forest.
Most of its economy is reliant on (i) exporting simple garments (women’s wear, men’s t- shirts, sweaters) and (ii) tourism. The garment factories are largely owned by foreign corporations. Its tourists are mostly Chinese, Vietnamese and Thai.
Unemployment is officially ‘low’. But many Cambodians are actually ‘underemployed’: they have jobs that could be easily lost, or work for their family or are farmers but have no salary.
The shock of COVID-19 has today severely affected its economy. Tourist arrivals has dried up, as has demand for its clothing exports.
Can Cambodia be developed into a better economy of the future? Can it be a prosperous model for other developing countries?
1. Outline a development plan for Cambodia. Do not only propose clever ideas. Discuss also some of the challenges in implementing them, if possible. A
Answer
Section 1:
1 (i). The Indonesian government can introduce domestic support policies like
- the price floor for the producers in the domestic market and
- provide some other domestic subsidy to the manufacturers of textile and leather footwear products, like tax reliefs, easy loans, etc.
(ii). The policies will ensure that the sellers receive a minimum price for their products in the domestic market. The price is usually above the free-market equilibrium price and hence increases the profit of the sellers. The subsidies helps in decreasing the cost of production and increase the domestic production. This will result in surplus at lower price which can be sold in the international market at competitive prices. As the imported goods will become expensive the domestic goods will become cheaper to the consumers.
(iii). The implementing of these polices will result in reduced international trade opportunities for the non-protected and developing countries where the government subsidies are not available to the producers. Since the government is putting no restrictions on import but supporting domestic industries, there is no need to worry.
2 (i). The trade balance chart of Indonesia for last 25 years shows an increasing trend over the long run. However there has been decline in the trade balance in recent years as compared from 2000’s.
(ii). The decrease in interest rate will
- make holding money less attractive and investment more attractive.
- will not attract the foreign funds and depreciate the currency against the US currency.
- The exports will become more attractive.
3. Indonesia export products are low complexity products mainly being the agriculture and minerals. However the research shows that if the exports product are more complex, they grow faster.
(i) The export sectors whose complexity can be improved are:
- paper which is used for graphic purposes,
- synthetic rubber,
- motor cars, engines,
- Electrical equipment like compressor, fans, electric shavers, integrated circuits, etc.
The products are already exported by the country and the country has the knowhow. They comprise the export basket of the country but are in very less percentage as compared to other less complex products.
(ii). These sectors can be improved in terms of complexity and value addition by
- More research and development in these sectors by the producers
- The government providing assistance and subsidies to these sectors
- Announcement of easy export policies for these products.
- The government can also place tariff on import of these products so that the domestic market is motivated.
Section 2
- Effect of Covid 19 pandemic and lockdown on Australian GDP is as follows:
- Consumption ( C)- The household spending on goods and service has reduced due to less movement of people and uncertainty of jobs. This is resulting in people to save more. The spending is only on essential products.
- Investment (I)- Investment in new houses and spending by firms in new business ventures is reduced. Due to reduced sales and demand the businesses are trying to maintain the existing infrastructure and avoid taking up new investments
- Government purchase (G) – the federal spending on goods and services has increased as the government is more inclined in upgrading the medical facilities and providing basic facilities to the needy and poor people affected by lockdown.
- Net Exports (NX)- The net exports has become almost zero. There is almost no imports and exports due to lockdown. Only essential products are traded.
2. Three main types of unemployment caused by Covid-19 lockdown are:
- Field operations: Due to social distancing and restricted movements, the field jobs are affected most by the lockdown. Thus the sales executives and marketing people are rendered jobless.
- Hotel/accommodation/ rental hiring of real estate are other types of jobs affected badly by the lockdown.
- Food services are also affected very badly due to the lockdown resulting in loss of jobs in the industry.
3. (i) AD and AS diagram to show the shift due to Covid- 19 pandemic lockdown: 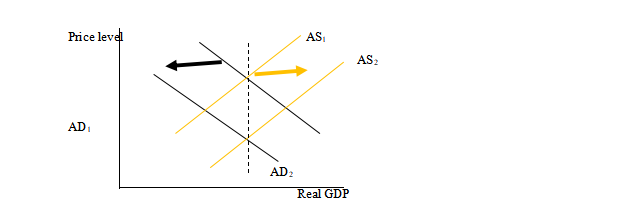
Real GDP
The average Demand (AD) has shifted to left (From AD 1 to AD2 as the demand has decreased and the investments has reduced. The aggregate supply curve (AS) has shifted to right (from AS 1 to AS2).The goods and labor is now available at cheaper rates. Thus for the same cost the goods produced are more and hence supply is higher. The increase in supply and decrease in demand leads to lower price level
(ii). From the diagram it is observed that the AD decreases due to fall in investments. There is loss of sales to the firms. The workers lose their jobs or have salary cuts. This further leads to decrease in demand of goods and services. The recession is recorded.
Due to recession, the workers are ready to work at lower salaries, the cost of inputs is reduced and hence the AS curve shifts to right. There are more goods produced at lower costs. The supply of goods and services increases.
It can be observed that the equilibrium is maintained at the same level of the GDP though at lower price level.
4. The cost of bread at the start of the year = $4
Inflation rate = 1.43%
Price at the end of the year = $4+ 1.43% of $4
= $4+ 0.0572 = $4.0572
The price of the bread loaf at the end of the year 2020 will be $4.0572
Section 3
- In order to develop the economy of the Cambodia, the country needs to make some structural changes to boost the development. Some of these changes can be to improve the supply side of the country, the government should focus on-
- Improving the education system of the county and introduce skill based education to make the adults employable.
- labor market reforms should be bought into place to ensure minimum wages to the workers and their welfare
- Incentives and tax rebates for technological research and development organization to promote technological improvements.
- Infrastructure development and urbanization of the country.
These measures will not only make the people of the country competent and able to produce goods and services but will also motivate them to produce better goods and services which can be exported. Two ways in which the development in the country can be started within the present functionalities are:
a. One way of starting is to produce organic products. The country has large forest areas and agriculture is a dominant occupation. This can be used for organic farming. The education and techniques of organic farming can be incorporated in the skill development plan of the country. The deterioration in environment has increased the demand of organic produce significantly.
This can be done by introducing development plans by the government like the industrial growth plans were started by Korean government to give its economy the boost. However the Cambodian government will face the internal barrier in implementing this due to the higher percentage of uneducated population. Therefore skill development plans as carried out in India are important in Cambodia too.
Making the presence of its products in the international market is another eternal barrier. This can be overcome by standardizing the products and following quality standards.
b. Improving the infrastructure of the country and urbanization is another way to boost the tourism industry of the country. The development of roads, transport and better hospitality industry will help in attracting tourists from rich countries like US and other European nations. The increase in tourism will increase the flow of foreign currency in the country and boost the economy.
However, the infrastructure development will need lots of funds which might be difficult for the government to acquire. It will also need labor extensively which the uneducated and idle people f the country might not like.
Section 4
- (i). The Pakistan government should implement expansionary fiscal policy. This would mean increasing government purchases or decreasing taxes. The government should follow both.
- The large population in the country is low income and unemployed. The decrease in taxes like the GST rate and sales tax will increase the spending power of the people as the goods will be cheaper. This will bring money in circulation. Demand for goods will increase and hence the production will increase. This will help in reducing the unemployment. The GDP of the country will also increase.
- The increase in government spending will improve the infrastructure and transport facility in the country. This will again help the manufacturers provide goods domestically at cheaper rates which is affordable by more people. The demand will increase and the cycle will start to rotate.
- Education and training can be the best supply side policy (SSP) for the government. It will not only improve the ability of the people to work but also reduce unemployment and improve the domestic production.
(ii). The limitation of the policy is the high government debt. And increasing GDP to debt ratio. This will make it difficult for the government to spend and that too with lower tax rates.
2.
(i) the country’s central bank will try to decrease the official interest rates. This will be make savings and holding of money less dearer. As the result there will be more spending and money will come in circulation with increased spending and investment. Lower interest rates will make borrowings cheaper and encourage investment by firms.
(ii). The central bank will reduce the interest rates by increasing the money supply. This is done by purchasing the securities. When the Central Bank buys the securities, the seller’s money is collected and deposited in the checking account. This money is given out on loans increasing the money supply.
(iii). The effect of the above action will be as follows:
(a) Consumer spending and business investment will increase. The interest rate will be lower so the will prefer to spend the money rather than saving it. Also the loans and borrowings will be available at lower rates, this will encourage business investment.
(b) GDP growth will increase. Business Investment will increase the production and consumer spending will increase the demand. There will be increase in GDP of the country.
(c) Unemployment will decrease. The increase in business investment and production will need more man power. Jobs will be created and unemployment will reduce.
(d) Inflation will increase. As the earnings and spending of the people will increase the purchasing power of money will decrease gradually and inflation will increase.










