- Home
- Free Samples
- Chemical Engineering
- EBS00101 Quantitative Analysis And In...
EBS00101 Quantitative Analysis and Industrial Chemistry Coursework 2 Answer

College of Engineering
Course Work -2
| Name of the programme | BEng NU |
| Name of Course with Code | General Chemistry for Engineering, EBS00101 |
| Coursework Type | Assignment Report |
| Assessment weightage | 50% |
| Aim |
|
| Learning Outcomes |
|
Task 1: Titration has been a versatile quantitative method of analyzing concentration of unknown solutions. Mention four types of titrations. Differentiate between conductometric and volumetric titration of acid and base. Answer should include comparison about apparatus, working procedure and advantages and disadvantages of both type of titrations. [Word limit 400, maximum marks 40]
Task 2: Rechargeable batteries has played a crucial role in making portable testing apparatus in chemical analysis laboratories. With the help of neatly labelled diagrams, discuss working principle, chemical reactions of charging and discharging, advantages and disadvantages of Lithium ion batteries. [Word limit 300, maximum marks 30]
Task 3: Draw a detailed organizational chart of various hydrocarbon families. Provide minimum one example of each family member and draw its molecular structure. [Word limit 100, maximum marks 20]
Task 4: Compare open and closed thermodynamic systems using suitable example and labelled diagrams. [Word limit 100, maximum marks 10]
Guidelines for Report Writing:
- Proper in text referencing should be followed and list of references should be provided at the end of the report.
- Diagrams can be hand drawn and copy pasted in word file or draw using drawing software. No copy paste allowed from internet. All diagram must contain student number at the bottom of diagram.
- Report should be typed in Arial 11 font size with justifies text. Headings should be mentioned in Bold.
- First Page of the report should include the title of the Coursework, student name and student number.
Answer
Task 1:
Titration has been a versatile quantitative method of analyzing the concentration of unknown solutions. Mention four types of titrations. Differentiate between conductometric and volumetric titration of acid and base. Answer should include comparison about apparatus, working procedure and advantages and disadvantages of both type of titrations. [Word limit 400, maximum marks 40]
Titration in Chemistry refers to the process that is used to determine the concentrations of the unknown solutions through the use of other known concentrated solutions (Cannan, 1942). Basically, there are 4 types of titrations. These are Precipitation titrations, Complexometric titrations, Redox titrations and Acid-base titrations.
Conductometric titration has applications in these given titrations which are complex titrations, precipitation titrations, redox titrations and acid-base titrations.
Whereas in Volumetric analysis (also known as titration)refers to the quantitative analysis in which the amount of a substance is determined by the measurement of the volume that the substance occupies (Anon., 2020).
Acid-Base type of Titration
This type of titration is majorly used in the determination of a specific acid content such as sodium hydroxide with a liquid. This is done by the addition of a reagent until the solution in the sample reaches a particular level of the pH. For instance, the use of the litmus paper can be used in this case scenario for the assessment of the change in color when the correct pH is reached.
Oxidation-Reduction Titration
In this type of titration which is also known as Redox relies on the loss or the gain of electrons within a sample to determine what is in the sample (Wilson, 1978). Oxidation-Reduction Titration can therefore be used in the study of concentration of metals within a solution or the study of contamination in drinking water.
Complexometric Titrations
In this type of titration, it can be useful in the determination of ingredients within detergents and soaps. It is therefore quite similar to precipitation titration in that a solid precipitate out of the sample when a reagent is added. The difference here however is that the solid is formed very fast after the reagent has been added. This reduces errors in measurement.
Precipitation Titrations
The main principle of the precipitation titrations is that the quantity of the added precipitating reagent or precipitant is equivalent to the substance being precipitated (Almeida, et al., 2000).
Within this type of titration, a reagent is added to the solution until a reaction happens. This occurs when a solid precipitate is formed from the solution during the addition of the reagent. This type of titration as a result helps to determine the concentrations of certain metals within any given sample or alternatively amounts of chloride within the drinking water.
Task 2:
Rechargeable batteries have played a crucial role in making a portable testing apparatus in chemical analysis laboratories. With the help of neatly labelled diagrams, discuss working principle, chemical reactions of charging and discharging, advantages and disadvantages of Lithium-ion batteries. [Word limit 300, maximum marks 30]
A battery refers to a series of cells or electrochemical cell that involve electrochemical Oxidation-Reduction reactions (Anon., 2020). It consists of electrolyte and two electrodes (cathode & anode)
The Discharge Process
Chemical energy is converted into electrical energy during the process of discharge. Atoms in the anode react with the Ions in the electrolyte which results in a buildup of electrons (Anon., 2020). This as a result causes the cathode to be positively charged whereas the anode becomes negatively charged.
Figure 1 Flow or Electrons in a cell
(Goodenough, 2012)
This is because the cathode undergoes reduction process, where there is a gain of electrons whereas the anode undergoes oxidation process since there is a loss of electrons (Ozawa, 2012).
The Recharging Process
For the recharging process to take place, electrical energy during the process of discharge is converted back to the Chemical energy (Anon., 2020).
In comparison to the traditional batteries; such batteries which are lithium-ion batteries are able to have a higher power density which enable it to have a higher battery life (Anon., 2020). In addition to that, these batteries not only can last longer but they can always be charged very fast (Goodenough, 2012).
Lithium-ion batteries however also has some of its shortcomings. Such shortcoming are related to the high costs, rates, energy, life and high density. When compared to the traditional rechargeable batteries which are known to be having good capabilities in terms of limited energy density given that the voltage for the long shelf-life is restricted to 1.5 V (Goodenough, 2012).
Task 3:
Draw a detailed organizational chart of various hydrocarbon families. Provide minimum one example of each family member and draw its molecular structure. [Word limit 100, maximum marks 20]
Hydrocarbons can be referred to as a compound of carbons and hydrogen with the Carbon atom being the main element of organic compounds (Elmhurst, 2020). These are;
Alkanes: Alkanes are the simplest among the hydrocarbons. An example to the Alkanes is Methane CH4
Figure 2 Ethane structure
Alkenes: As for the alkenes, they have a carbon to carbon double bond. An example Ethene C2H4
Figure 3 Ethene C2H4 structure
Alkynes: have a carbon to carbon triple bond. An example to the Alkynes is Ethyne C2H2
Figure 4 Ethyne structure
Cycloalkanes: These are isomers of alkenes which do not contain a carbon to carbon double bond. An example of Cycloalkanes is Cyclopropane C3H6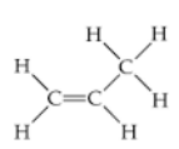
Figure 5: Cycloalkanes structure
Task 4:
Compare open and closed thermodynamic systems using suitable example and labelled diagrams. [Word limit 100, maximum marks 10]
Figure 6: Thermodynamic system
(Anon., 2019).
The Open system is a system that both their energy as well as mass are able to flow through the boundaries of system. As a result, they are also known as control volume (Anon., 2019). A good example of such a system is the water heater which allows for the cold water to enter into the system whereas.
A closed system is that which has energy flowing through them while their masses remains fixed (Anon., 2019). A good example of such a system is the gas-filled in container and a movable piston is a closed system as changing the volume by adjusting the piston results in change in temperature of the gas.










