- Home
- Free Samples
- Pedagogies
- CHCECE017 Foster Holistic Development...
CHCECE017 Foster Holistic Development and Wellbeing of Child in Early Childhood Assessment Answer

Inform Learning and Foster Development Cluster
CHCECE017 Foster the holistic development and wellbeing of the child in early childhood (2)
CHCECE023 Analyse information to inform learning (2)
CHC30113 – Certificate III Early Childhood Education and Care (4)
CHC50013- Certificate III Early Childhood Education and Care (4)
Assessment instructions
| Assessment details | Instructions |
| Assessment overview | The objective of this clustered assessment is to assess your knowledge and performance in the following units:
|
| Instructions for this assessment | This assessment is in one part and also contains Evidence Guides and Assessment Feedback (marking tools):
You must read the entire document before commencing your assessment so you are aware of all requirements. |
Introduction
To achieve a satisfactory result for this assessment:
- You must read through each task so you understand what you need to complete.
- You must research and analyse information from at least two different, credible sources to complete each part of the task.
- You must identify and discuss the relevance of this research to the early childhood education and care context including the process of monitoring children’s learning and development.
When: Complete and submit your written assessment by the specified due date.
Where: You may complete the assessment task in the classroom, home or online environment.
Resources and equipment: Pens, paper and/or computer if typing assessment.
Assessment must ensure the use of:
- National Quality Framework for Early Childhood Education and Care;
- The relevant approved learning framework under the National Quality Framework for Early Childhood Education and Care; and
- Credible sources of early childhood information:
Suggested credible sources of early childhood information to complete the research task:
Task 3 – Core Principles of Child Development
Brief:
Research and analyse information from at least two (2) credible sources to address the following:
- In table a) below;
- Identify and summarise the core principles of child development and associated developmental tasks
- Provide an outline of the five developmental domain areas
- Describe the link between all areas of development.
(800 - 1000 words)
- In table b) below;
- Explain the term ‘holistic approach’.
- Discuss how holistic practice supports the link between developmental domains?
(200 words)
- In table c) below;
- Identify, and describe the contextual factors that influence children’s emotional and psychological development
- Explain why it is important to understand this concept as an educator.
(200 words)
- In table d) below;
- Define self-identity and self-esteem
- Describe the factors that enhance their development
- Explain why it is important to understand this concept as an educator.
(200 words)
| Research and findings: |
Table a)
1. Identify and summarise the core principles of child development and associated developmental tasks |
2. The five Developmental domains |
3. The link between all areas of development |
| TABLE B) i. Explain the term ‘holistic approach’. |
| ii.Describe the link between all areas of development? |
Table c)
1. Identify, and describe the contextual factors which influence children’s emotional and psychological development |
2. Explain why it is important to understand this concept as an educator. |
Table d)
1. Define self-identity and self-esteem. |
2. Describe the factors that enhance their development |
3. Explain why it is important to understand this concept as an educator |
Task 4 – Monitor children’s learning and development
Brief:
Research and analyse information from at least two (2) credible sources to address the following:
- In table a) below describe the process of monitoring and assessing children’s holistic development, learning and wellbeing you must
- Explain why we assess and monitor children’s learning and development.
- Explain what informs and guides this process
- Describe how we ensure that information and observations are gathered and used to inform planning for all children
- Explain inclusive assessment practices
- Describe the role of summative assessment in this process (300 words)
- In table b) below describe how will an educator collaborate with families and colleagues to support children’s learning? (50 words)
- In table c) below describe a process to reflect on and improve your own practices as you monitor children’s learning and development. (200 words)
| Research and findings: |
Table a)
1. Explain why we assess and monitor children’s learning and development |
2. Explain what informs and guides this process |
3. Describe how we ensure that information and observations are gathered and used to inform planning for all children |
4. Explain inclusive assessment practices |
5. Describe the role of summative assessment in this process |
Table b)
1. How will an educator collaborate with colleagues and families to support children’s learning? |
Table c)
2. Describe a process to reflect on and improve your own practices as you monitor children’s learning and development |
Answer
I) 1. Principle of Cephalo-caudal/ Development proceeds from the head downwards
This principle is concerned about the direction for growth.
This principle states that development proceeds from head to toe and from six months to twelve months, occurring sequentially (Social and Economic Development”, 2019).
Developmental task: infants learn head movement first and eventually face movement followed by arm movements. Till 12 months infant gains leg co-ordinations including crawling standing and walking,
2. Principle of Proximodistal development
This principle states that Development goes from centre to the periphery of body, this means that the spinal cord develops first followed by further development of the other organs and functions. This principle deals with the flow of body growth. An appropriate environment explores the stimulation pushing child for the development to the potential.
Developmental task: Arm develops before the hand and legs develop before fingers and toes.
3. Development is dependent on the maturation and learning
Maturation is the sequence of biological growth that occurs in the child. This growth opens the new possibilities and abilities for him. The changes in the brain enable the child to improve the cognitive and learning function.
Developmental task: once the child develops the motor function he/she can use a pencil and draw things. A child of 12 months old can use languages and words with the development of the brain.
4. Development occurs from simple to more complex
This principle is concerned with the development of cognitive powers, problem-solving and communications skills. This enables the child to learn the relation between things.
A child of 18 months can tell that oranges and apples are round but in coming months he can differentiate that apples are red and oranges are orange.
5. Growth and development is a continuous process
There is the continuous addition of skills to the already acquired one. This decides the further basis of the achievements.
Developmental task: The infant can move and lift his head followed by the movement of the limbs and then grasping the objects and by the age of four, he is able of climb up the stairs and draw by holding colours in hands.
6. Growth and development is from general to specific
First movements and function of the child is generalized uni-direction and reflective followed by specificity toward object
Developmental task: A child first can only hold the object with his hand further moving to use only his fingers by the age of four.
7. There is an individual rate of growth and development
Each child develops at a different rate from another.
Developmental task: child intellectual may be developed at 10 months whereas the motor skills may develop at 12 months similarly a child may learn to walk at 9 months whereas other may at 12 months.
ii) Adaptive domain
This is the domain where a child derives information from the other domains and uses this information. All these skills and information leads to better participation of the child in day to day activity and routine Adaptive skills also enhance the ability of a child to get well versed with the new environment and enhancing past familiar activity. The adaptive domain includes self-care like skills required for feeding, dressing, toileting and eating.
Personal social Domain
This allows a child in engaging in meaningful interaction involving society and surrounding including peers and adults (Ruffin, 2017). This domain includes a better understanding of the self emotions as well others. As this skill domain develops child have a better understanding of relationships, empathy and self-awareness.
Communication domain
This domain deals with child ability to analyze the situation and respond to it using language. As this domain develops child become more responsive to the instruction of the instructions of the adult.
Motor domain
In this domain, there is the use of muscular activity. The child here learns to take control of the functioning of large and small muscles of the body. Like walking, standing and running. These motor skills fine skills (cutting paper with scissors), gross skills climbing stairs, walking) and perceptual skills (drawing, writing)
Cognitive Domain
This is usually associated with the ability often individual child to learn, remember and problem-solving. This domain is the intellectual understand and processing of the information. This redirects the child toward academic activities. This domain may include attention to the details and memory, reasoning, understanding of concepts example counting, matching, rhymes learning etc (Department of education 2009).
III)
All domains of childhood development are interconnected with each other for example ability to interact in the social surrounding is impacted by the ability of the child to learn new information. The adaptive domain is related to the cognitive and motor domain example performing the self-care routine and activities may require the motor domain of the child. Also for understanding and responding to the new environment may include the cognitive domain skills like learning, memory and problem-solving.
Delay in the social development skill may affect the participation activities thus affect other domain skills. For example, a child which has not developed the motor skills or communication skill may face difficulty in social interactions ( Houwen et al., 2016).
The development of communicative domain is impaired by faulty personal social interactions. In turn, imparted communicative domain affects the ability of the academic activities of the child that is the following the instructions. Hence the failure of this domain may lead to an impact on the motor learning skills, socio-personal skills as well as adaptive skills.
The motor domain is the ability to use muscles thus deciding the response of the child to the environment impacting the adaptive domain of the child. For example, motor activities of the child example standing, balancing ay impact his adaption to the new environment. On the other hand, adaptive skills like eating food in a particular utensil are directly associated with motor skills like fine small muscle functioning. Persona social skill too is linked to the motor skills and child’s social interactions example, playing in a social setting may include the use of the large muscles ( Maccoby & Martin, 1999).
c) i). The holistic approach of child development addresses the physical, emotional, intellectual and spiritual dimensions of the child life ( Bronfenbrenner & Morris, 2006). A child learns various things at various stages of life. Hence accounting for a holistic approach is required for understanding the overall development of a child in every area.
ii) In the development of the child social, physical, spiritual, emotional and cultural dimension plays a crucial role. The holistic approach encompasses the overall developmental domain in the acquisition of interdependent skills. This means that in growth and development of a child physical surrounding, adaptive powers, emotional skill, and relationships with adult plays a major role. A holistic approach addressed a child as a learning individual who has various interlinked dimensions of interaction, learning, problem-solving and understanding rather than just an individual task. One domain skills set learning is highly dependent on the other in an influential manner for overall development. For example, Holistic approach addresses the spiritual dimension within a child life that is the cultural social interactions which may impact the personal social and communication domain of development.
D) i) Family environment: This plays an important role in the development of child social behaviour and adjustments (Sameroff 2009).
Parent-child interactions: This includes parent behaviour, emotional expression of parent or caregivers
Socio-economic status: This is represented by the annual income, education in the family as well as the occupation.
The environment at school/ relation with the educator or teacher
Relationship with the peer
ii) Instability of a child in terms of economic and environment at home exposes to the lesser accessibility of the resources as well as the learning facilities. Contextual factors may disrupt the development of cognitive function with behavioural competencies. Risk of children exhibiting classroom behaviour problem is higher when they are exposed to contextual factors. Knowledge of these contextual factors and their negative impact helps in better intervention planning (Myers & Pianta 2008). For example, children with low socioeconomic status may have pre-academic skills at one standard below average. Understanding of factors helps in Co-operation with teacher allowing better learning in classroom settings, academic success, self-control, cooperation, compliance and relationships (Hindman et al., 2010).
D) i) Self-esteem is defined as the negative or positive attitude of the individual toward self. Self-identity refers to the self-cognition that people impose on themselves as the result of social behavior, position and responsibilities they hold. For example, a woman can be a mother; blood donor or teacher (Rosenberg & Owen, 2001). This may include personal name, gender, occupation, roles and ethnicity.
ii) Factors
Age: The concept of self-esteem and self-identity keep on changing with age
Gender, Education, Media: Example anorexia can result from a certain type of body image depicted in media, Culture example in western culture focus is more on self dependencies and auto concept of self whereas in Asian culture interdependence is the major self factor.
Physical illness
iii) Role of the educator is crucial as implementation techniques enhancing the quality of life and social resources. Knowledge may contribute in professional activities within the classroom. For example, the educator can focus teaching to develop abilities, personality, traits and motivation self responsibilities, appreciations, discipline and encouragements (Zlatkovic et al., 2012). Also, the educator can facilitate acceptance to peer pressure, realistic towards goals, accept criticisms positively, and learn from their mistakes. The educator should relate to these concepts to assess the gift, capabilities, flaws, strength and weakness of the individual child and release their significance and potential.
A) i) Holistic assessment and monitoring is the process of information collection from varied sources, synthesis of this Information and then planning educational strategies based on this information. It furnishes the information related to the physical, emotional, behavioral, adaptive and social, skills strength. It helps in identifying the need for assistance or help. It also helps the educator in forming the educational plan as per the need of the child with parents and community in the collaborative effort.
ii) A holistic approach is governed by, time availability, structural support to educator, policies, management support and knowledge of educator.
iii) To ensure the accurate collection and use of the information we should
-Keep the value of cultural influences on the learning of the children. As children are greatly influenced by the cultural background
-The basis of collecting information should be based on the daily activities of the chills so that an accurate picture is developed.
-Define objectives
- Make close observations
- Incorporate the views of the children on the learning process. Also, the perspective of families and caregivers should be taken in the account.
- Should be done through various approaches and techniques.
- Should focus on the child as a whole.
-Should be accurate and non-judgmental
Iv ) The approach of inclusive assessment practices the activities planned to demonstrate the learning objectives by giving various opportunities. It has exercises focusing on self-assessment and self-awareness and open feedback from child. Participants are open in providing ideas, perspectives and their thinking process.
v) Summative assessments are designed to get information regarding understanding. For example journals, portfolios etc. feedback is also included where the purpose is a more focused peer and self-evaluations hence provide an inclusive outlook of assessment.
b) An educator can collaborate with families and colleagues to support children’s learning by
- Establishing a secure, respectful and reciprocal relationship with them
-Valuing their contribution and feedback in the child learning
-Communicating openly and respectful with each other
-Discuss the perspectives about each child
-Engage in mutual decision-making
c) The process of reflection allows the educator to honestly assess their professional practices as well as ideas to enhance the learning experience for future purposes (Ferreira, Keliher & Blomfield, 2013). Reflective practices provide better knowledge on how things are happing and point out the good practices educator are following or area for improvements. Kobs suggested four stages reflective process that has concrete experience, doing the reflective observation including reviewing the experience. Followed by abstract or conceptualization (learning from the experience) then experimentation with what have been learnt. 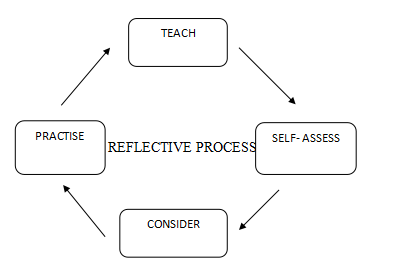
How it helps in improving
As an educator the process helps in a better understanding of the classroom setting as being not merely set of students but the diversity of thinking process. Focus on personal histories, group discussions to improve practices. Valuing of addressing questions like what, why and when to achieve and observe collective information. Giving valuable weightage to peer opinions as they can provide insight to the whole process as well the area where improvements are required (Sellars, 2012). It helps in understanding our own practice, area for required improvement, skills for the improvement and approaches to achieve the implementation. Further it allow educator to
-Collecting information including identification of the issue on the topic, gathering the information, try to have the feedback of other professionals, families and even children.
-Ask questions and analyze the answers
-Focus on goals addressed, achievements and outcomes of monitoring practice,
-Evaluating informedjudgmentsaboutpractice, basedonevidence










